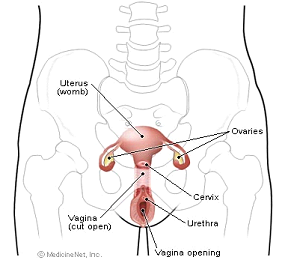
What is the cervix?
The cervix is part of a woman’s reproductive system. It’s in the pelvis. The cervix is the lower, narrow part of the uterus (womb).
The cervix is a passageway:
- The cervix connects the uterus to the vagina. During a menstrual period, blood flows from the uterus through the cervix into the vagina. The vagina leads to the outside of the body.
- The cervix makes mucus. During sex, mucus helps sperm move from the vagina through the cervix into the uterus.
- During pregnancy, the cervix is tightly closed to help keep the baby inside the uterus. During childbirth, the cervix opens to allow the baby to pass through the vagina.
Cervical cancer begins in cells on the surface of the cervix. Over time, the cervical cancer can invade more deeply into the cervix and nearby tissues. The cancer cells can spread by breaking away from the original (primary) tumor. They enter blood vessels or lymph vessels, which branch into all the tissues of the body. The cancer cells may attach to other tissues and grow to form new tumors that may damage those tissues. The spread of cancer is called metastasis. See the Staging section for information about cervical cancer that has spread.
Risk factors and causes of cervical cancer
Studies have found a number of factors that may increase the risk of cervical cancer. For example, infection with HPV (human papillomavirus) is the main cause of cervical cancer. HPV infection and other risk factors may act together to increase the risk even more:
- HPV infection: HPV is a group of viruses that can infect the cervix. An HPV infection that doesn’t go away can cause cervical cancer in some women. HPV is the cause of nearly all cervical cancers.
HPV infections are very common. These viruses are passed from person to person through sexual contact. Most adults have been infected with HPV at some time in their lives, but most infections clear up on their own.
Some types of HPV can cause changes to cells in the cervix. If these changes are found early, cervical cancer can be prevented by removing or killing the changed cells before they can become cancer cells. The NCI fact sheet Human Papillomaviruses and Cancer: Questions and Answers has more information.
A vaccine for females ages 9 to 26 protects against two types of HPV infection that cause cervical cancer.
Human papillomavirus (HPV) infection of the cervix can lead to cervical cancer. A vaccine designed to prevent cervical cancer and other diseases caused by infection with HPVs was approved for use in the U.S. in June 2006. This is the first vaccine to be developed against a known risk factor for the development of a cancer.
While some HPV types infect the skin and cause benign warts and other lesions, about 40 types of HPVs can infect the genital tract. Genital HPV infection is very common in the general population; estimates suggest that up to 50% of all sexually active people will be infected at some point in their lives. In the majority of cases, the infection does not cause any symptoms, but in some women, HPV infection can progress to cause precancerous and cancerous lesions of the uterine cervix. HPVs that infect the genital area are also associated with other less common genital cancers in men and women such as cancers of the anus, vagina, penis, and vulva. HPV infection also causes genital warts in men and women.
The most common HPV types that infect the genital area are HPV types 6, 11, 16, and 18. Among these, HPV types 6 and 11 are most commonly associated with benign lesions, such as genital warts and mild precancerous changes of the cervix. In contrast, HPV types 16 and 18 are the types found in the majority of cancers as well as in severe precancerous changes of the cervix. The vaccine, called Gardasil, targets these four common HPV types.
- Smoking: Among women who are infected with HPV, smoking cigarettes slightly increases the risk of cervical cancer.
- Weakened immune system: Infection with HIV (the virus that causes AIDS) or taking drugs that suppress the immune system increases the risk of cervical cancer.
- Sexual history: Women who have had many sexual partners have a higher risk of developing cervical cancer. Also, a woman who has had sex with a man who has had many sexual partners may be at higher risk of developing cervical cancer. In both cases, the risk of developing cervical cancer is higher because these women have a higher risk of HPV infection.
- Having many children: Studies suggest that giving birth to many children (5 or more) may slightly increase the risk of cervical cancer among women with HPV infection.
Having an HPV infection or other risk factors does not mean that a woman will develop cervical cancer. Most women who have risk factors for cervical cancer never develop it.
Symptoms
- Abnormal vaginal bleeding
- Bleeding that occurs between regular menstrual periods
- Bleeding after sexual intercourse, douching, or a pelvic exam
- Menstrual periods that last longer and are heavier than before
- Bleeding after going through menopause
- Increased vaginal discharge
- Pelvic pain
- Pain during sex
Infections or other health problems may also cause these symptoms. Only a doctor can tell for sure. A woman with any of these symptoms should tell her doctor so that problems can be diagnosed and treated as early as possible.
Abnormal vaginal bleeding
Detection and diagnosis
Finding and treating abnormal cells can prevent most cervical cancer. Also, the Pap test can help find cancer early, when treatment is more likely to be effective.
For most women, the Pap test is not painful. It’s done in a doctor’s office or clinic during a pelvic exam. The doctor or nurse scrapes a sample of cells from the cervix. A lab checks the cells under a microscope for cell changes. Most often, abnormal cells found by a Pap test are not cancerous. The same sample of cells may be tested for HPV infection.
If you have abnormal Pap or HPV test results, your doctor will suggest other tests to make a diagnosis:
- Colposcopy: The doctor uses a colposcope to look at the cervix. The colposcope combines a bright light with a magnifying lens to make tissue easier to see. It is not inserted into the vagina. A colposcopy is usually done in the doctor’s office or clinic.
- Biopsy: Most women have tissue removed in the doctor’s office with local anesthesia. A pathologist checks the tissue under a microscope for abnormal cells.
- Punch biopsy: The doctor uses a sharp tool to pinch off small samples of cervical tissue.
- LEEP: The doctor uses an electric wire loop to slice off a thin, round piece of cervical tissue.
- Endocervical curettage: The doctor uses a curette (a small, spoon-shaped instrument) to scrape a small sample of tissue from the cervix. Some doctors may use a thin, soft brush instead of a curette.
- Conization: The doctor removes a cone-shaped sample of tissue. A conization, or cone biopsy, lets the pathologist see if abnormal cells are in the tissue beneath the surface of the cervix. The doctor may do this test in the hospital under general anesthesia.
Removing tissue from the cervix may cause some bleeding or other discharge. The area usually heals quickly. Some women also feel some pain similar to menstrual cramps. Your doctor can suggest medicine that will help relieve your pain.
Staging
When cancer spreads from its original place to another part of the body, the new tumor has the same kind of cancer cells and the same name as the original tumor. For example, if cervical cancer spreads to the lungs, the cancer cells in the lungs are actually cervical cancer cells. The disease is metastatic cervical cancer, not lung cancer. For that reason, it’s treated as cervical cancer, not lung cancer. Doctors call the new tumor “distant” or metastatic disease.
Your doctor will do a pelvic exam, feel for swollen lymph nodes, and may remove additional tissue. To learn the extent of disease, the doctor may order some of the following tests:
- Chest x-rays: X-rays often can show whether cancer has spread to the lungs.
- CT scan: An x-ray machine linked to a computer takes a series of detailed pictures of your organs. A tumor in the liver, lungs, or elsewhere in the body can show up on the CT scan. You may receive contrast material by injection in your arm or hand, by mouth, or by enema. The contrast material makes abnormal areas easier to see.
- MRI: A powerful magnet linked to a computer is used to make detailed pictures of your pelvis and abdomen. The doctor can view these pictures on a monitor and can print them on film. An MRI can show whether cancer has spread. Sometimes contrast material makes abnormal areas show up more clearly on the picture.
- PET scan: You receive an injection of a small amount of radioactive sugar. A machine makes computerized pictures of the sugar being used by cells in your body. Cancer cells use sugar faster than normal cells, and areas with cancer look brighter on the pictures.
The stage is based on where cancer is found. These are the stages of invasive cervical cancer:
- Stage I: The tumor has invaded the cervix beneath the top layer of cells. Cancer cells are found only in the cervix
- Stage II: The tumor extends to the upper part of the vagina. It may extend beyond the cervix into nearby tissues toward the pelvic wall (the lining of the part of the body between the hips). The tumor does not invade the lower third of the vagina or the pelvic wall.
- Stage III: The tumor extends to the lower part of the vagina. It may also have invaded the pelvic wall. If the tumor blocks the flow of urine, one or both kidneys may not be working well.
- Stage IV: The tumor invades the bladder or rectum. Or the cancer has spread to other parts of the body.
- Recurrent cancer: The cancer was treated, but has returned after a period of time during which it could not be detected. The cancer may show up again in the cervix or in other parts of the body.
Treatment
The choice of treatment depends mainly on the size of the tumor and whether the cancer has spread. The treatment choice may also depend on whether you would like to become pregnant someday.
Your doctor can describe your treatment choices, the expected results of each, and the possible side effects. You and your doctor can work together to develop a treatment plan that meets your medical and personal needs.
Your doctor may refer you to a specialist, or you may ask for a referral. You may want to see a gynecologic oncologist, a surgeon who specializes in treating female cancers. Other specialists who treat cervical cancer include gynecologists, medical oncologists, and radiation oncologists. Your health care team may also include an oncology nurse and a registered dietitian.
Before treatment starts, ask your health care team about possible side effects and how treatment may change your normal activities. Because cancer treatments often damage healthy cells and tissues, side effects are common. Side effects may not be the same for each person, and they may change from one treatment session to the next.
At any stage of the disease, supportive care is available to relieve the side effects of treatment, to control pain and other symptoms, and to help you cope with the feelings that a diagnosis of cancer can bring.
Surgery
Surgery is an option for women with Stage I or II cervical cancer. The surgeon removes tissue that may contain cancer cells:
- Radical trachelectomy: The surgeon removes the cervix, part of the vagina, and the lymph nodes in the pelvis. This option is for a small number of women with small tumors who want to try to get pregnant later on.
- Total hysterectomy: The surgeon removes the cervix and uterus.
- Radical hysterectomy: The surgeon removes the cervix, some tissue around the cervix, the uterus, and part of the vagina.
With either total or radical hysterectomy, the surgeon may remove other tissues:
- Fallopian tubes and ovaries: The surgeon may remove both fallopian tubes and ovaries. This surgery is called a salpingo-oophorectomy.
- Lymph nodes: The surgeon may remove the lymph nodes near the tumor to see if they contain cancer. If cancer cells have reached the lymph nodes, it means the disease may have spread to other parts of the body.
The time it takes to heal after surgery is different for each woman. You may have pain or discomfort for the first few days. Medicine can help control your pain. Before surgery, you should discuss the plan for pain relief with your doctor or nurse. After surgery, your doctor can adjust the plan if you need more pain control.
After a radical trachelectomy, some women have bladder problems for a few days. The hospital stay usually is about 2 to 5 days.
After a hysterectomy, the length of the hospital stay may vary from several days to a week. It is common to feel tired or weak for a while. You may have problems with nausea and vomiting, and you may have bladder and bowel problems. The doctor may restrict your diet to liquids at first, with a gradual return to solid food. Most women return to their normal activities within 4 to 8 weeks after surgery.
After a hysterectomy, women no longer have menstrual periods. They cannot become pregnant.
When the ovaries are removed, menopause occurs at once. Hot flashes and other symptoms of menopause caused by surgery may be more severe than those caused by natural menopause. You may wish to discuss this with your doctor before surgery. Some drugs have been shown to help with these symptoms, and they may be more effective if started before surgery.
For some women, a hysterectomy can affect sexual intimacy. You may have feelings of loss that make intimacy difficult. Sharing these feelings with your partner may be helpful. Sometimes couples talk with a counselor to help them express their concerns.
Radiation therapy
Radiation therapy (also called radiotherapy) is an option for women with any stage of cervical cancer. Women with early stage cervical cancer may choose radiation therapy instead of surgery. It also may be used after surgery to destroy any cancer cells that remain in the area. Women with cancer that extends beyond the cervix may have radiation therapy and chemotherapy
Radiation therapy uses high-energy rays to kill cancer cells. It affects cells only in the treated area.
Doctors use two types of radiation therapy to treat cervical cancer. Some women receive both types:
- External radiation therapy: A large machine directs radiation at your pelvis or other tissues where the cancer has spread. The treatment usually is given in a hospital or clinic. You may receive external radiation 5 days a week for several weeks. Each treatment takes only a few minutes.
- Internal radiation therapy: A thin tube is placed inside the vagina. A radioactive substance is loaded into the tube. You may need to stay in the hospital while the radioactive source is in place (up to 3 days). Or the treatment session may last a few minutes, and you can go home afterward. Once the radioactive substance is removed, no radioactivity is left in your body. Internal radiation may be repeated two or more times over several weeks.
Side effects depend mainly on how much radiation is given and which part of your body is treated. Radiation to the abdomen and pelvis may cause nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, or urinary problems. You may lose hair in your genital area. Also, your skin in the treated area may become red, dry, and tender.
You may have dryness, itching, or burning in your vagina. Your doctor may advise you to wait to have sex until a few weeks after radiation treatment ends.
You are likely to become tired during radiation therapy, especially in the later weeks of treatment. Resting is important, but doctors usually advise patients to try to stay as active as they can.
Although the side effects of radiation therapy can be upsetting, they can usually be treated or controlled. Talk with your doctor or nurse about ways to relieve discomfort.
It may also help to know that most side effects go away when treatment ends. However, you may wish to discuss with your doctor the possible long-term effects of radiation therapy. For example, the radiation may make the vagina narrower. A narrow vagina can make sex or follow-up exams difficult. There are ways to prevent this problem. If it does occur, however, your health care team can tell you about ways to expand the vagina.
Another long-term effect is that radiation aimed at the pelvic area can harm the ovaries. Menstrual periods usually stop, and women may have hot flashes and vaginal dryness. Menstrual periods are more likely to return for younger women. Women who may want to get pregnant after radiation therapy should ask their health care team about ways to preserve their eggs before treatment starts.
Chemotherapy
For the treatment of cervical cancer, chemotherapy is usually combined with radiation therapy. For cancer that has spread to distant organs, chemotherapy alone may be used.
Chemotherapy uses drugs to kill cancer cells. The drugs for cervical cancer are usually given through a vein (intravenous). You may receive chemotherapy in a clinic, at the doctor’s office, or at home. Some women need to stay in the hospital during treatment.
The side effects depend mainly on which drugs are given and how much.
- Blood cells: When chemotherapy lowers the levels of healthy blood cells, you’re more likely to get infections, bruise or bleed easily, and feel very weak and tired. Your health care team will check for low levels of blood cells. If your levels are low, your health care team may stop the chemotherapy for a while or reduce the dose of drug. There are also medicines that can help your body make new blood cells.
- Cells in hair roots: Chemotherapy may cause hair loss. If you lose your hair, it will grow back, but it may change in color and texture.
- Cells that line the digestive tract: Chemotherapy can cause a poor appetite, nausea and vomiting, diarrhea, or mouth and lip sores. Your health care team can give you medicines and suggest other ways to help with these problems.
Other side effects include skin rash, tingling or numbness in your hands and feet, hearing problems, loss of balance, joint pain, or swollen legs and feet. Your health care team can suggest ways to control many of these problems. Most go away when treatment ends.
Chemotherapy kills fast-growing cancer cells, but the drugs can also harm normal cells that divide rapidly: